
1. 태풍의 정의와 발생 원리
태풍은 열대 지방에서 발생하는 강력한 기상 현상으로, 바람의 세기와 비가 많이 내리는 특징을 가지고 있습니다. 태풍은 해양에서 발생한 후, 열대 저기압이 발달하면서 회전하는 형태로 진화합니다. 이 회전은 지구의 코리올리 효과에 의해 발생하는데, 코리올리 효과는 지구의 자전에 의해 발생하는 힘으로, 북반구에서는 오른쪽으로, 남반구에서는 왼쪽으로 회전하는 현상입니다. 태풍은 바다 위에서 발생하며, 따라서 바다의 온도와 습도가 태풍의 발생과 진화에 영향을 미칩니다. 태풍은 주로 열대 지방에서 발생하지만, 일부 경우에는 일본이나 중국과 같은 동아시아 지역까지 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다. 태풍은 강력한 바람과 폭우를 동반하며, 이로 인해 큰 피해를 초래할 수 있습니다. 따라서 태풍에 대한 적절한 대비와 대응이 필요합니다.
2. 태풍의 경로 예측을 위한 기상학적 요소
태풍의 경로 예측은 매우 중요한 과제이다. 이를 위해 기상학적 요소들을 분석하고 예측 모델을 구축해야 한다. 태풍의 경로는 다양한 요소들에 의해 결정되는데, 주로 태풍의 위치, 기압, 바람의 방향과 세기, 해수면 온도 등이 영향을 미친다. 이러한 요소들을 고려하여 태풍의 경로를 예측하는 모델을 개발하고, 이를 통해 사전에 대비할 수 있는 시간을 확보하는 것이 중요하다. 또한, 태풍의 경로 예측은 인간의 생명과 재산을 보호하는데 큰 역할을 한다. 따라서, 기상학적 요소들을 철저히 분석하고 예측 모델을 개발하여 태풍의 경로 예측 정확도를 높이는 것이 필요하다.
3. 태풍의 강도 측정과 분류 기준
태풍은 강한 바람과 폭우를 동반한 자연재해로, 많은 피해를 야기할 수 있습니다. 따라서 태풍의 강도를 정확히 측정하고 분류하는 것은 매우 중요합니다. 태풍의 강도는 일반적으로 바람의 세기를 기준으로 측정됩니다. 바람의 세기는 풍속계를 사용하여 측정되며, 일반적으로 초속(m/s) 단위로 표시됩니다.
태풍의 강도를 분류하기 위해서는 일정한 기준이 필요합니다. 국제기상기구(WMO)에서는 태풍의 강도를 다섯 가지로 분류하고 있습니다. 가장 약한 강도인 "열대저압"은 풍속이 17m/s 이하일 때로 정의되며, 이는 태풍의 초기 단계를 의미합니다. 그 다음으로는 "강한 열대저압"으로 풍속이 18m/s 이상 24.4m/s 이하일 때로 분류됩니다. 이후 "태풍"으로 분류되는 강도는 풍속이 24.5m/s 이상 32.6m/s 이하일 때입니다. "강태풍"은 풍속이 32.7m/s 이상 41.4m/s 이하일 때로 분류되며, 가장 강한 강도인 "초강태풍"은 풍속이 41.5m/s 이상일 때로 정의됩니다.
태풍의 강도 측정과 분류는 기상청과 국제기상기구 등의 기상기관에서 주
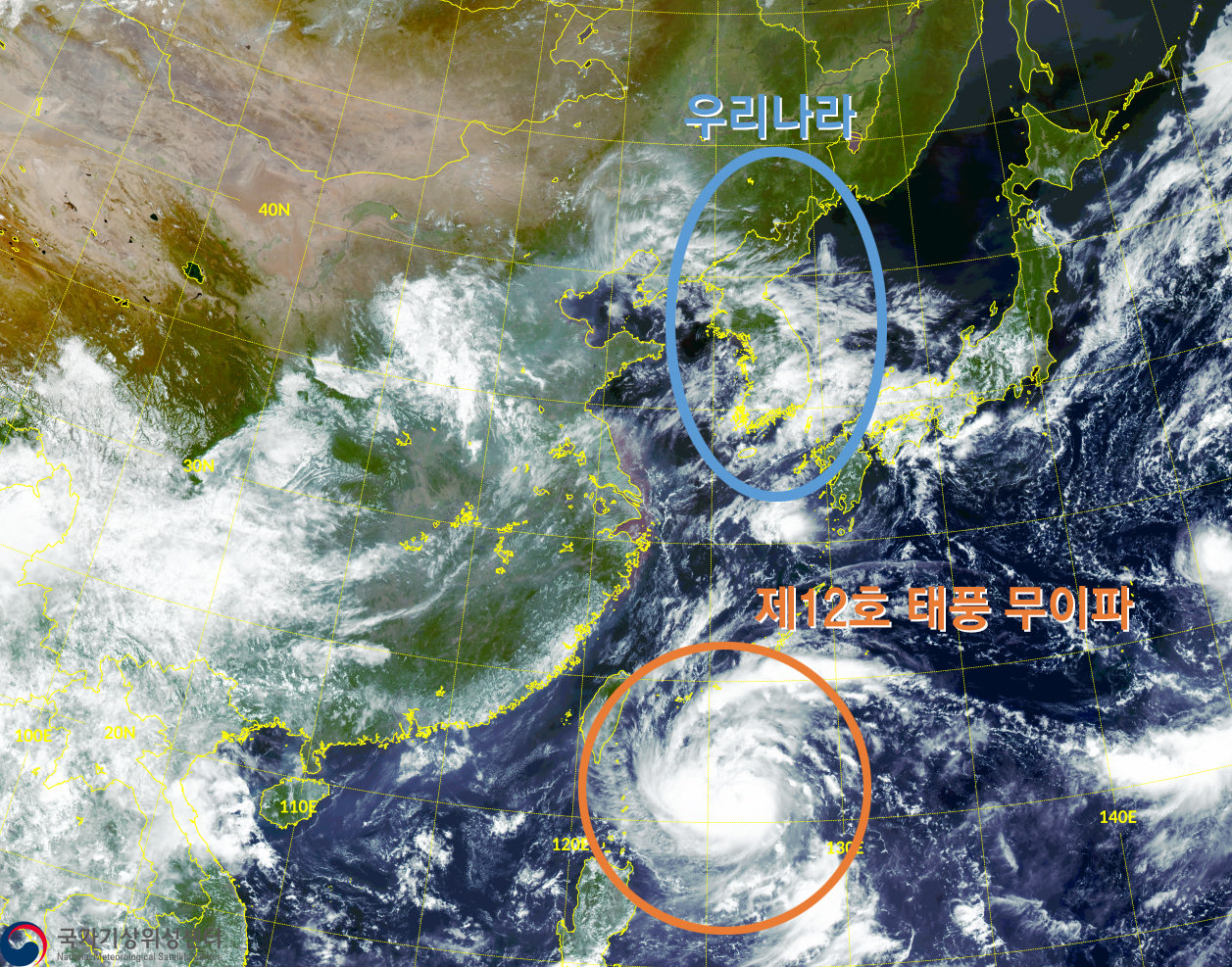
4. 태풍 경로 추적을 위한 기상위성과 레이더 시스템
태풍 경로 추적을 위해 기상위성과 레이더 시스템은 매우 중요한 역할을 합니다. 기상위성은 대기 상태를 촬영하여 태풍의 위치와 크기를 파악하는 데 사용됩니다. 이를 통해 태풍의 이동 경로와 강도를 예측할 수 있습니다.
레이더 시스템은 기상 조건을 실시간으로 감지하고 태풍의 위치와 강도를 정확하게 측정하는 데 사용됩니다. 레이더는 전자기파를 발사하여 대기 중의 물체와의 반사 신호를 측정합니다. 이를 통해 태풍의 중심과 강도를 정확하게 파악할 수 있습니다.
기상위성과 레이더 시스템은 서로 보완적인 역할을 하며, 태풍의 경로 추적에 매우 유용합니다. 이를 통해 태풍으로 인한 피해를 최소화하고 대응 조치를 미리 할 수 있습니다. 따라서 태풍 관련 기상 정보를 신속하게 수집하고 분석하는 기상 관측 시스템의 개선이 필요합니다.
5. 태풍 경로 추적의 중요성과 예방 대책
태풍은 매년 여러 지역에서 큰 피해를 야기하는 자연재해 중 하나입니다. 태풍이 발생하면 많은 사람들이 피해를 입고, 재산이 파괴되며, 인명 피해도 발생합니다. 이러한 이유로 태풍의 경로 추적은 매우 중요합니다.
태풍의 경로 추적은 기상청과 관련 기관들이 주로 담당하고 있습니다. 기상청은 태풍의 발생과 이동 경로를 예측하여 관련 정보를 제공합니다. 이를 통해 주민들은 태풍의 도래를 미리 예측하고 대비할 수 있습니다.
태풍의 예방 대책은 다양한 형태로 이루어집니다. 가장 기본적인 예방 방법은 태풍이 다가올 때 안전한 장소로 대피하는 것입니다. 또한, 주변 환경을 정리하고, 외부에서 날아오는 물체나 나무 등을 고정시키는 등의 조치도 필요합니다.
또한, 태풍에 대비하여 비상 대피 계획을 수립하는 것도 중요합니다. 대피 경로와 대피 시설을 미리 파악하고, 가족 구성원들과 소통하여 대피 계획을 공유하는 것이 좋습니다.
마지막으로, 태풍에 대비하여 생활용품과 식량 등을 미리 준비하는 것도 필요합니다. 긴급 상황에 대비하여 충분한 양의 식량과 생활용
태풍, 열대, 기상, 바람, 비, 회전, 코리올리 효과, 지구, 자전, 북반구, 남반구, 바다, 온도, 습도, 일본, 중국, 동아시아, 대비, 대응, 경로, 예측, 기상학적, 위치, 기압, 방향, 세기, 해수면, 경로 예측, 모델, 사전 대비, 생명, 재산, 강도, 측정, 분류, 풍속, 초속, 열대저압, 강한 열대저압, 태풍, 강태풍, 초강태풍, 기상청, 국제기상기구, 기상위성, 레이더, 실시간, 중심, 피해, 대응 조치, 기상 관측 시스템, 예방, 대책, 안전한 장소, 대피, 환경 정리, 비상 대피 계획, 대피 경로, 대피 시설, 생활용품, 식량
1. Definition of typhoon and how it occurs
A typhoon is a powerful weather phenomenon that occurs in tropical regions and is characterized by strong winds and heavy rain. Typhoons originate in the ocean and then evolve into a rotating form as a tropical cyclone develops. This rotation is caused by the Earth's Coriolis effect, which is a force generated by the Earth's rotation, causing it to rotate to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere. Typhoons occur over the ocean, and therefore ocean temperature and humidity affect the occurrence and evolution of typhoons. Typhoons mainly occur in tropical regions, but in some cases they can affect areas as far as East Asia, such as Japan and China. Typhoons bring strong winds and heavy rain and can cause significant damage. Therefore, proper preparation and response to typhoons is necessary.
2. Meteorological factors for predicting the path of a typhoon
Predicting the path of a typhoon is a very important task. For this purpose, meteorological factors must be analyzed and a prediction model must be built. The path of a typhoon is determined by various factors, mainly the location of the typhoon, atmospheric pressure, wind direction and strength, and sea surface temperature. It is important to develop a model that predicts the path of a typhoon by considering these factors and thereby secure time to prepare in advance. Additionally, predicting the path of a typhoon plays a major role in protecting human life and property. Therefore, it is necessary to thoroughly analyze meteorological factors and develop a forecast model to improve the accuracy of predicting the path of a typhoon.
3. Typhoon intensity measurement and classification criteria
A typhoon is a natural disaster accompanied by strong winds and heavy rain and can cause a lot of damage. Therefore, it is very important to accurately measure and classify the intensity of typhoons. The intensity of a typhoon is usually measured based on wind strength. Wind strength is measured using an anemometer and is usually expressed in speed per second (m/s).
Certain standards are required to classify the intensity of typhoons. The International Meteorological Organization (WMO) classifies the intensity of typhoons into five categories. The weakest intensity, a “tropical cyclone,” is defined as wind speeds of 17 m/s or less, signifying the early stages of a typhoon. Next, it is classified as a "strong tropical depression" when the wind speed is 18 m/s or more and 24.4 m/s or less. Hereafter, the intensity classified as a "typhoon" is when the wind speed is 24.5 m/s or more but 32.6 m/s or less. A “strong typhoon” is classified as a wind speed of 32.7 m/s or more and 41.4 m/s or less, and the strongest “super typhoon” is defined as a wind speed of 41.5 m/s or more.
Typhoon intensity measurement and classification are conducted by meteorological organizations such as the Korea Meteorological Administration and the International Meteorological Organization.
4. Weather satellite and radar system for tracking typhoon paths
Meteorological satellites and radar systems play a very important role in tracking typhoon paths. Meteorological satellites are used to determine the location and size of typhoons by imaging atmospheric conditions. This allows us to predict the typhoon's path and intensity.
Radar systems are used to detect weather conditions in real time and accurately measure the location and intensity of typhoons. Radar emits electromagnetic waves and measures their reflections from objects in the atmosphere. This allows you to accurately determine the center and intensity of the typhoon.
Meteorological satellites and radar systems complement each other and are very useful in tracking the path of typhoons. Through this, we can minimize damage caused by typhoons and take response measures in advance. Therefore, there is a need to improve weather observation systems that quickly collect and analyze typhoon-related weather information.
5. Importance of tracking typhoon paths and preventive measures
Typhoons are one of the natural disasters that cause great damage to many regions every year. When a typhoon occurs, many people are affected, property is destroyed, and lives are lost. For this reason, tracking the path of typhoons is very important.
The Korea Meteorological Administration and related organizations are mainly responsible for tracking the path of typhoons. The Korea Meteorological Administration predicts the occurrence and movement path of typhoons and provides related information. This allows residents to predict and prepare for the arrival of typhoons.
Typhoon prevention measures come in various forms. The most basic prevention method is to evacuate to a safe place when a typhoon approaches. In addition, measures such as cleaning up the surrounding environment and fixing objects or trees flying in from outside are also necessary.
It is also important to have an emergency evacuation plan in case of a typhoon. It is a good idea to identify evacuation routes and evacuation facilities in advance, and communicate with family members to share your evacuation plan.
Lastly, it is also necessary to prepare daily necessities and food in advance in preparation for a typhoon. Sufficient food and living supplies for emergencies
Typhoons, tropics, weather, wind, rain, rotation, Coriolis effect, Earth, rotation, northern hemisphere, southern hemisphere, sea, temperature, humidity, Japan, China, East Asia, contrast, response, path, forecast, meteorological, location, atmospheric pressure, Direction, intensity, sea level, path prediction, model, advance preparation, life, property, intensity, measurement, classification, wind speed, per second, tropical depression, strong tropical depression, typhoon, strong typhoon, super typhoon, Korea Meteorological Administration, International Meteorological Organization, meteorological satellite , radar, real-time, central, damage, response measures, weather observation system, prevention, countermeasures, safe place, evacuation, environmental clearance, emergency evacuation plan, evacuation route, evacuation facilities, daily necessities, food
1. 台風の定義と発生原理
台風は熱帯地方で発生する強力な気象現象で、風の強さと雨の多い特徴を持っています。台風は海洋で発生した後、熱帯低気圧が発達しながら回転する形に進化します。この回転は地球のコリオリ効果によって発生し、コリオリ効果は地球の自転によって発生する力で、北半球では右に、南半球では左に回転する現象です。台風は海の上で発生し、したがって、海の温度と湿度は台風の発生と進化に影響を与えます。台風は主に熱帯地方で発生しますが、場合によっては日本や中国などの東アジア地域まで影響を及ぼす可能性があります。台風は強力な風と大雨を伴い、これにより大きな被害を招く可能性があります。したがって、台風に対する適切なコントラストと対応が必要です。
2.台風の経路予測のための気象学的要素
台風のルート予測は非常に重要な課題です。そのためには、気象学的要素を分析し、予測モデルを構築する必要があります。台風の経路は様々な要因によって決まり、主に台風の位置、気圧、風の方向と強度、海面温度などが影響します。これらの要因を考慮して台風の経路を予測するモデルを開発し、これにより事前に備えられる時間を確保することが重要である。さらに、台風の経路予測は、人間の生命と財産を保護するのに大きな役割を果たします。したがって、気象要素を徹底的に分析し、予測モデルを開発して台風の経路予測精度を高めることが必要です。
3. 台風の強度測定と分類基準
台風は強い風と大雨を伴う自然災害で、多くの被害を引き起こす可能性があります。したがって、台風の強度を正確に測定して分類することは非常に重要です。台風の強さは、一般的に風の強さに基づいて測定されます。風の強さは風速計を使用して測定され、通常は秒速(m / s)単位で表示されます。
台風の強度を分類するには、一定の基準が必要です。国際気象機関(WMO)では、台風の強度を5つに分類しています。最も弱い強度の「熱帯低圧」は、風速が17m / s以下のときと定義され、これは台風の初期段階を意味します。次は「強い熱帯低圧」で、風速が18m/s以上24.4m/s以下のときに分類されます。以後「台風」に分類される強度は、風速が24.5m/s以上32.6m/s以下の時です。 「強台風」は風速が32.7m / s以上41.4m / s以下のときに分類され、最も強い強度の「超強台風」は風速が41.5m / s以上のときと定義されます。
台風の強度測定と分類は、気象庁や国際気象機関などの気象機関で
台風経路追跡のための気象衛星とレーダーシステム
台風経路を追跡するために、気象衛星とレーダーシステムは非常に重要な役割を果たします。気象衛星は台風の撮影と台風の位置と大きさを把握するために使用されます。これにより、台風の移動経路と強度を予測することができます。
レーダーシステムは、気象条件をリアルタイムで検出し、台風の位置と強度を正確に測定するために使用されます。レーダは電磁波を発射して大気中の物体との反射信号を測定する。これにより、台風の中心と強度を正確に把握できます。
気象衛星とレーダーシステムは互いに補完的な役割を果たし、台風の経路追跡に非常に役立ちます。これにより、台風による被害を最小限に抑え、対応措置を事前に行うことができます。したがって、台風に関連する気象情報を迅速に収集し分析する気象観測システムの改善が必要である。
5. 台風経路追跡の重要性と予防対策
台風は、毎年さまざまな地域で大きな被害を引き起こす自然災害の1つです。台風が発生すると多くの人が被害を受け、財産が破壊され、人命被害も発生します。このため、台風のルート追跡は非常に重要です。
台風の経路追跡は、気象庁や関連機関が主に担当しています。気象庁は台風の発生と移動経路を予測し、関連情報を提供します。これにより、住民は台風の到来を事前に予測して準備することができます。
台風の予防対策は様々な形で行われます。最も基本的な予防方法は、台風が近づくときに安全な場所に避難することです。また、周辺環境を整理し、外部から飛ぶ物や木などを固定するなどの措置も必要です。
また、台風に備えて緊急避難計画を策定することも重要です。避難経路と避難施設を事前に把握し、家族のメンバーと交流して避難計画を共有することをお勧めします。
最後に、台風に備えて生活用品や食料などを事前に準備することも必要です。緊急事態に備えて、十分な量の食料と生活用
台風、熱帯、気象、風、雨、回転、コリオリ効果、地球、自転車、北半球、南半球、海、温度、湿度、日本、中国、東アジア、コントラスト、対応、ルート、予測、気象学的、位置、気圧、方向、世紀、海面、ルート予測、モデル、事前コントラスト、生命、財産、強度、測定、分類、風速、秒速、熱帯低圧、強い熱帯低圧、台風、強台風、超強台風、気象庁、国際気象機関、気象衛星、レーダー、リアルタイム、中心、被害、対応措置、気象観測システム、予防、対策、安全な場所、避難、環境整理、緊急避難計画、避難経路、避難施設、生活用品、食料


'잡학다식' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 태풍의 위험성과 대비 방법 (0) | 2023.11.21 |
|---|---|
| 태풍의 위험성과 대비 방법 (0) | 2023.11.20 |
| 태풍의 정의와 발생 원리 (0) | 2023.11.18 |
| 태풍의 정의와 기상 현상 설명 (1) | 2023.11.17 |
| 태풍의 정의와 기상 현상 설명 (0) | 2023.11.16 |



